General account ,
structure and functions of bacterial cells :
(NOTE : SHORT
QUESTIONS CAN BE IN THE FORM OF BOLD LETTERS IN THE NOTES)
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek is regarded as “ father of bacteriology” because he first time (1683) observed these
tiny ‘animalcules’ from the scum of teeth of a man. Bacteria are cosmopolitan
in distribution, occur every where in water , air, soil, food stuffs etc. Bacteria are prokaryotic, achlorophyllous and u nicellular organism. Instead of
true chlorophyll, bacteria may containbacterio chlorophyll and chlorobium chlorophyll. Normally, the
bacteria may ranges between 1 to 5 um. It posses the foloowing forms:-
Ø
Cocci(spherical) – Eg.Micrococcus, Diplococcus
Ø
Bacilli(rod shaped)- Eg. Diphobacilli, Streptobacilli
Ø
Spirilla (spirally coiled) – Eg. Spirochaete, Spirillum
Ø
Vibrio(comma shaped) – Eg. Vibrio cholera
On the basis of flagella , bacteria are :-
Ø
Atrichous(no flagella )
Ø
Monotrichous(single flagellum at each end)
Ø
Amphitrichous(one flagellum at each end)
Ø
Cephalotrichous(tuft of flagella at each pole)
Ø
Lophotrichous(tuft of flagella at each pole)
Ø
Peratrichous(several flagella all over the
surface)
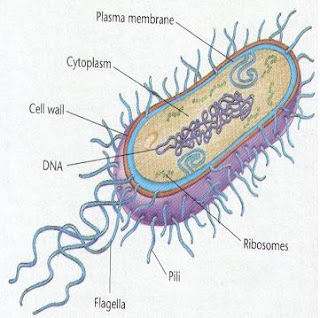
Structure
and functions :
A typical bacterial cell is enveloped by 3 distinct layers :
Capsule (slime layer) , cell wall and cell membrane. Capsuleis theoutermost protective layer against the adverse climatic
condition and toxic substances present with in host. It posses the complex cell wall composed up of proteins, carbohydrate and chitin but
cellulose is absent inner to cell wall lies cell membrane which serve as a
permeability barrier and surrounds protoplast. The cytoplasm spreads uniformly
through out the cell and contains many vacuoles, food granules; ribosome,
mesosomes and incipient nucleus(having
no major cytoplasmic organelles i.e. mitochondria, lysosome, endoplasmic
reticulum, nuclear membrane etc.). The mesosome
are circular bodies helps in separation
of replicated DNA during nuclear division and are site of respiration. Bacteria
posses one or more thread like structure
called flagella originating from the
cytoplasm. Such bacteria are motile in nature. Bacterial nucleus is quite
primitive type, lacks nucleolus, nuclear membrane, nuclear sap etc. Some gram –ve bacteria posses fine hair like
protoplasmic out growths called fimbriae, scattered over the entire surface of
bacterial cell.
Concept of
autotrophic and heterotrophic life cycles :
On the basis of mode of nutrition, Bacteria are of two types
:
Heterotrophic bacteria
: Most of the bacteria are heterotrophic in nutrition, cannot synthesis their
food from simple inorganic substances.
These
are of three types :
Ø
Parasitic
bacteria : Parasitic bacteria take their food
from host which may be obligate or facultative parasites.
Ø
Saprophytic
bacteria : These types of bacteria take their
food from dead organic matter and are found growing in animals dung decaying
vegetables etc. It secretes and breaks the complex food into simpler and
soluble forms.
Ø
Symbiotic
bacteria : Some bacteria like Rhizobium
species occur as symbionts on the root nodulues of leguminous plants.
(Note :- Symbiotic
means both the partners or the organisms are equally benefited by the symbiotic
bacteria.)
Autotrophic bacteria : These
type of bacteria synthesize thir food themselves from inorganic substances.
The energy is either obtained
chemically called chemotropic or from solar radiation called photo autotrophic forms. While
manufacturing food, chemoautotrophic bacteria obtain energy from chemicals; do
not require solar energy but the photoautotrophic (photosynthetic) bacteria
posses chlorobium chlorophyll and bacterio chlorophyll which trap solar energy.
Bacterial photosynthesis takes in light
but in absence of oxygen.
Koch’s postulates
a.
The specific organism should be shown to be
present in all cases of animals suffering from a specific disease but should
not be found in healthy animals.
b.
The specific micro organism should be isolated
from the diseased animal and grow on artificial laboratory media.
c.
This freshly isolated micro organism when
inoculated into a heat laboratory animal should cause the same disease seen in
the original animal.
d.
The micro organism should be reisolated in pure
culture from the experimental infection.
Gram
positive bacteria
|
Gram
negative bacteria
|
They retain the deep blue or purple
with crystal violet and subsequently with potassium iodide and alcohol.
|
They do not retain the color when
treated with potassium iodide and alcohol.
|
The cell wall is 100 to 200 0A.
|
The cell wall is 70 to 1200A.
|
Peptidoglycan constitutes the 70% of
cell wall.
|
Peptidoglycan constitutes the 30 % of
the cell wall.
|
They are generally susceptible to
lysosomes or antibiotics.
|
They are generally resistant to
lysosomes or antibiotics.
|
Generally they do not bear fimbriae or
sex pili.
|
Generally they bear pili or fimbriae.
|
Cell membrane forms mesosomes.
|
Mesosomes are absent.
|
Economic importance
(Note : While writing the economic importance example i.e
scientific names are compulsory.)
Beneficial activities
:-
a.
Some species of bacteria like Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Chlostridium
,Azotobacter, fix atmospheric nitrogen in usable forms for plants.
b.
Some species of clostridium are used in
manufacturing of Vitamin B(riboflavin).
c.
Lactic acid bacteria(Streptococcus lactis) help in coagulation of milk.
d.
Three types of medicine – antibiotics, antisera
and vaccines are formed by bacteria.
e.
Bacteria(E.
coli) present in human colon synthsize vitamin B and releases it form human
use.
f.
Bacteria help in digestion in herbivores animals
in the digestion of cellulose. Bacillus subtilis produces the enzymes amylase
and protease.
g.
By the activity of clostridium the butyl alcohol
and acetone are obtained form sugar molasses.
h.
It helps in fibers retting of jute, coconut and
other fibrous plants.
i.
Bacteria like Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus ramosus etc. decompose complex organic
compounds like proteins into ammonium compound . These are also known as
ptrefying bacteria.
Harmful activities :-
a.
Many human diseases such as diarrhoea,
meningitis, pneumonia etc. are caused by pathogenic bacteria.
b.
Some denitrifying bacteria reduce the soil
fertility by depleting the nitrogen contents of soil.
c.
Some bacteria spoils food stuffs, leather and
wooden articles.
d.
Certain bacteria destroy the activity of
penicillin by producing an enzyme penicillinase.
e.
Tuberculosis of cattle, anthrax of sheep is
caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and
Bacillus anthracis respectively.
f.
Citrus canker by Xanthomonas citri, ring rot of
potato by cornebacterium sepedonieum etc.
g.
Spirochete cytophoga destroys cotton and article
made from it.
HSEB QUESTIONS
VERY SHORT QUESTIONS: (1
Marks each)
Ø
Give the function of mesosomes of a bacterial
cell.
Ø
How do the bacteria get their nutrition?
ANSWER IN BRIEF : (3
Marks each)
Ø
Give the economic importance of bacteria.
Ø
Discuss the agricultural economic importance of
bacteria.
Plz comment
ReplyDelete